Android Glide 图片加载库
2023-07-21, by alamide
Glide 图片加载库。
本文学习的目标:
-
缓存策略
-
生命周期监听
-
内存复用策略
-
大图加载
一行简单的图片请求代码
Glide.with(this).load("https://himg.bdimg.com/sys/portrait/item/pp.1.1fdc338e.ric5F8oKJekRIoc8wsplCg?_t=1689664631126").into(imageView);
1.缓存策略
Glide 可以分为内存缓存、磁盘缓存两大类,其中内存缓存又可以加一级 ActiveResources ,磁盘缓存又可以加一级 ResourceCache,对变换(裁剪、裁剪等)后的图片缓存。
Glide 对数据源分了五类,在 DataSource 中有定义,有 LOCAL、REMOTE、DATA_DISK_CACHE、RESOURCE_DISK_CACHE、MEMORY_CACHE。
-
LOCAL 本地资源,如 assets、drawable
-
REMOTE 远程资源,如网络资源
-
DATA_DISK_CACHE 磁盘缓存
-
RESOURCE_DISK_CACHE 对原数据进行处理后的磁盘缓存
-
MEMORY_CACHE 内存缓存
Glide 磁盘缓存有多种策略,所有策略都在 DiskCacheStrategy 中有定义,包括 ALL、NONE、DATA、RESOURCE、AUTOMATIC。
-
ALL 为缓存所有,包括原数据和最终显示在页面上的图片
-
NONE 不对任何资源进行磁盘缓存
-
DATA 只缓存原数据
-
RESOURCE 缓存显示的数据,同一张图片,对不同大小的 ImageView 会有多个磁盘缓存
-
AUTOMATIC 自动选择,保存原数据和变换后的数据,为 Glide 默认使用的磁盘缓存策略
1.1 资源缓存
本部分主要来追踪 Glide 是如何对,网络请求的数据是如何缓存的,什么是三级缓存(或称为四级缓存)。追踪的代码起点为读取远程网络的资源其主要的请求逻辑在 DecodeJob 中
class DecodeJob<R> implements DataFetcherGenerator.FetcherReadyCallback,
Runnable, Comparable<DecodeJob<?>>, Poolable {
public void run() {
runWrapped();
}
private void runWrapped() {
//初始时 runReason 为 INITIALIZE
switch (runReason) {
case INITIALIZE:
stage = getNextStage(Stage.INITIALIZE);
currentGenerator = getNextGenerator();
runGenerators();
break;
case SWITCH_TO_SOURCE_SERVICE:
runGenerators();
break;
case DECODE_DATA:
decodeFromRetrievedData();
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized run reason: " + runReason);
}
}
private Stage getNextStage(Stage current) {
switch (current) {
case INITIALIZE:
//默认磁盘缓存可以 decodeCachedResource
return diskCacheStrategy.decodeCachedResource()
? Stage.RESOURCE_CACHE
: getNextStage(Stage.RESOURCE_CACHE);
case RESOURCE_CACHE:
return diskCacheStrategy.decodeCachedData()
? Stage.DATA_CACHE
: getNextStage(Stage.DATA_CACHE);
case DATA_CACHE:
// Skip loading from source if the user opted to only retrieve the resource from cache.
return onlyRetrieveFromCache ? Stage.FINISHED : Stage.SOURCE;
case SOURCE:
case FINISHED:
return Stage.FINISHED;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unrecognized stage: " + current);
}
}
private void runGenerators() {
currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
startFetchTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
boolean isStarted = false;
//这边的逻辑依次磁盘中获取 RESOURCE_CACHE、DATA_CACHE
while (!isCancelled
&& currentGenerator != null
&& !(isStarted = currentGenerator.startNext())) {
stage = getNextStage(stage);
currentGenerator = getNextGenerator();
//因为是第一次请求,所以最终会走到 stage == Stage.SOURCE
if (stage == Stage.SOURCE) {
//再次调用 DecodeJob.run()
reschedule();
return;
}
}
// We've run out of stages and generators, give up.
if ((stage == Stage.FINISHED || isCancelled) && !isStarted) {
notifyFailed();
}
}
public void reschedule() {
runReason = RunReason.SWITCH_TO_SOURCE_SERVICE;
//再次调用 DecodeJob.run()
callback.reschedule(this);
}
}
网络请求的逻辑是先去磁盘中读取 ResourceCache ,没有命中目标,再读取 DataCache,如果还是没有命中目标,则接下来会去进行网络请求。下面就进行网络请求的代码追踪,此时 runReason = RunReason.SWITCH_TO_SOURCE_SERVICE,stage = Stage.SOURCE,currentGenerator = SourceGenerator
class DecodeJob<R> implements DataFetcherGenerator.FetcherReadyCallback,
Runnable, Comparable<DecodeJob<?>>, Poolable {
public void run() {
runWrapped();
}
private void runWrapped() {
switch (runReason) {
case SWITCH_TO_SOURCE_SERVICE:
runGenerators();
break;
}
}
private void runGenerators() {
//执行 SourceGenerator.startNext();
currentGenerator.startNext();
}
}
class SourceGenerator implements DataFetcherGenerator, DataFetcherGenerator.FetcherReadyCallback {
public boolean startNext() {
//初次执行时 dataToCache 为 null
if (dataToCache != null) {
Object data = dataToCache;
dataToCache = null;
cacheData(data);
}
if (sourceCacheGenerator != null && sourceCacheGenerator.startNext()) {
return true;
}
sourceCacheGenerator = null;
loadData = null;
boolean started = false;
while (!started && hasNextModelLoader()) {
loadData = helper.getLoadData().get(loadDataListIndex++);
//fetcher 负责具体的加载工作,这里使用 HttpUrlFetcher 其为 DataSource.REMOTE
if (loadData != null
&& (helper.getDiskCacheStrategy().isDataCacheable(loadData.fetcher.getDataSource())
|| helper.hasLoadPath(loadData.fetcher.getDataClass()))) {
started = true;
startNextLoad(loadData);
}
}
return started;
}
private void startNextLoad(final LoadData<?> toStart) {
loadData.fetcher.loadData(
helper.getPriority(),
//会在 HttpUrlFetcher 准备好 inputStream 后回调 onDataReady()
new DataCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public void onDataReady(@Nullable Object data) {
//这里
if (isCurrentRequest(toStart)) {
onDataReadyInternal(toStart, data);
}
}
@Override
public void onLoadFailed(@NonNull Exception e) {
if (isCurrentRequest(toStart)) {
onLoadFailedInternal(toStart, e);
}
}
});
}
void onDataReadyInternal(LoadData<?> loadData, Object data) {
DiskCacheStrategy diskCacheStrategy = helper.getDiskCacheStrategy();
//loadData.fetcher.getDataSource() 为 DataSource.REMOTE
if (data != null && diskCacheStrategy.isDataCacheable(loadData.fetcher.getDataSource())) {
//需要缓存的数据
dataToCache = data;
//再次调用 DecodeJob.run()
cb.reschedule();
}
}
}
去网络请求时,会先去准备输入流,然后开始准备缓存,再次调用 DecodeJob.run()
class DecodeJob<R> implements DataFetcherGenerator.FetcherReadyCallback,
Runnable, Comparable<DecodeJob<?>>, Poolable {
public void run() {
runWrapped();
}
private void runWrapped() {
case SWITCH_TO_SOURCE_SERVICE:
runGenerators();
}
private void runGenerators() {
//currentGenerator 仍为 SourceGenerator
currentGenerator.startNext();
}
}
class SourceGenerator implements DataFetcherGenerator, DataFetcherGenerator.FetcherReadyCallback {
public boolean startNext() {
//前一次的 startNext 已经将 dataToCache 赋值为 InputStream 了,所以不为空
if (dataToCache != null) {
Object data = dataToCache;
dataToCache = null;
cacheData(data);
}
//调用 DataCacheGenerator.startNext()
if (sourceCacheGenerator != null && sourceCacheGenerator.startNext()) {
return true;
}
}
private void cacheData(Object dataToCache) {
Encoder<Object> encoder = helper.getSourceEncoder(dataToCache);
DataCacheWriter<Object> writer =
new DataCacheWriter<>(encoder, dataToCache, helper.getOptions());
originalKey = new DataCacheKey(loadData.sourceKey, helper.getSignature());
//向磁盘中缓存数据,具体存储的类为 DiskLruCacheWrapper
helper.getDiskCache().put(originalKey, writer);
sourceCacheGenerator = new DataCacheGenerator(Collections.singletonList(loadData.sourceKey), helper, this);
}
}
class DataCacheGenerator implements DataFetcherGenerator, DataFetcher.DataCallback<Object> {
public boolean startNext() {
cacheFile = helper.getDiskCache().get(originalKey);
//使用 ByteBufferFileLoader.ByteBufferFetcher 加载数据,加载成功之后回调 onDataReady()
loadData.fetcher.loadData(helper.getPriority(), this);
}
public void onDataReady(Object data) {
//回调 DecodeJob 的 onDataFetcherReady
cb.onDataFetcherReady(sourceKey, data, loadData.fetcher, DataSource.DATA_DISK_CACHE, sourceKey);
}
}
public class DiskLruCacheWrapper implements DiskCache {
//做具体的存储任务
public void put(Key key, Writer writer) {
//文件名先以 .tmp 结尾
writer.write(file);
//重命名文件名,去掉 .tmp
editor.commit();
}
}
到这里网络请求的逻辑是,现将网络中请求的数据存储到文件中,再将文件中的文件读取到 ByteBuffer 中,之后再次回到 DecodeJob 中,回调其中的 onDataFetcherReady
class DecodeJob<R> implements DataFetcherGenerator.FetcherReadyCallback,
Runnable, Comparable<DecodeJob<?>>, Poolable {
public void onDataFetcherReady(
Key sourceKey, Object data, DataFetcher<?> fetcher, DataSource dataSource, Key attemptedKey) {
//做一些“解码”工作,将 bytes 转换为 Bitmap,或对原图进行采样
decodeFromRetrievedData();
}
private void decodeFromRetrievedData() {
Resource<R> resource = null;
resource = decodeFromData(currentFetcher, currentData, currentDataSource);
}
private <Data> Resource<R> decodeFromData(
DataFetcher<?> fetcher, Data data, DataSource dataSource) throws GlideException {
//解码原文件
Resource<R> result = decodeFromFetcher(data, dataSource);
}
private <Data> Resource<R> decodeFromFetcher(Data data, DataSource dataSource)
throws GlideException {
LoadPath<Data, ?, R> path = decodeHelper.getLoadPath((Class<Data>) data.getClass());
return runLoadPath(data, dataSource, path);
}
private <Data, ResourceType> Resource<R> runLoadPath(
Data data, DataSource dataSource, LoadPath<Data, ResourceType, R> path)
throws GlideException {
Options options = getOptionsWithHardwareConfig(dataSource);
DataRewinder<Data> rewinder = glideContext.getRegistry().getRewinder(data);
return path.load(rewinder, options, width, height, new DecodeCallback<ResourceType>(dataSource));
}
<Z> Resource<Z> onResourceDecoded(DataSource dataSource, @NonNull Resource<Z> decoded) {
//来判断是否需要缓存 Resource,即变换后的 bitmap
if (diskCacheStrategy.isResourceCacheable(isFromAlternateCacheKey, dataSource, encodeStrategy)) {
if (encoder == null) {
throw new Registry.NoResultEncoderAvailableException(transformed.get().getClass());
}
final Key key;
switch (encodeStrategy) {
case SOURCE:
key = new DataCacheKey(currentSourceKey, signature);
break;
case TRANSFORMED:
key =
new ResourceCacheKey(
decodeHelper.getArrayPool(),
currentSourceKey,
signature,
width,
height,
appliedTransformation,
resourceSubClass,
options);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown strategy: " + encodeStrategy);
}
LockedResource<Z> lockedResult = LockedResource.obtain(transformed);
//先准备好,等待后续执行缓存
deferredEncodeManager.init(key, encoder, lockedResult);
result = lockedResult;
}
return result;
}
}
public class LoadPath<Data, ResourceType, Transcode> {
public Resource<Transcode> load(DataRewinder<Data> rewinder, @NonNull Options options, int width,
int height, DecodePath.DecodeCallback<ResourceType> decodeCallback) throws GlideException {
return loadWithExceptionList(rewinder, options, width, height, decodeCallback, throwables);
}
private Resource<Transcode> loadWithExceptionList(DataRewinder<Data> rewinder, @NonNull Options options, int width,
int height, DecodePath.DecodeCallback<ResourceType> decodeCallback, List<Throwable> exceptions) throws GlideException {
Resource<Transcode> result = null;
result = path.decode(rewinder, width, height, options, decodeCallback);
}
}
public class DecodePath<DataType, ResourceType, Transcode> {
public Resource<Transcode> decode(DataRewinder<DataType> rewinder, int width, int height,
@NonNull Options options, DecodeCallback<ResourceType> callback) throws GlideException {
//使用 ImageView 的 width,height 来“解码” Bitmap,有可能原图很大,而要显示的 ImageView 很小,所以需要采样
//来节约内存
Resource<ResourceType> decoded = decodeResource(rewinder, width, height, options);
//需要展示的 Bitmap 生成,回调解码完成的方法,最终还是会回到到 DecodeJob.onResourceDecoded()
//会去做一些转换工作,还会判断是否会存储转换后的 Bitmap,存储策略为 ATOMIC 时,只存储修改后的图片,如裁剪、变换,不会存储采样后的图片
//而存储策略为 ALL 时,会存储所有变换的图片
Resource<ResourceType> transformed = callback.onResourceDecoded(decoded);
//BitmapDrawableTranscoder
//return LazyBitmapDrawableResource.obtain(resources, toTranscode);
return transcoder.transcode(transformed, options);
}
}
上面这部分的主要工作是对磁盘中缓存的文件进行变换,包括对原图进行采样、变换等,最终返回 LazyBitmapDrawableResource,还有就是判断是否需要缓存变化后的图片,如果需要缓存则进行初始化工作。到这里图片已经全部处理完毕了,返回的也是最终会显示在屏幕的图片。
接下来就是编码完成后的工作了,再次回到 DecodeJob,
class DecodeJob<R> implements DataFetcherGenerator.FetcherReadyCallback,
Runnable, Comparable<DecodeJob<?>>, Poolable {
private void decodeFromRetrievedData() {
if (resource != null) {
notifyEncodeAndRelease(resource, currentDataSource);
} else {
runGenerators();
}
}
private void notifyEncodeAndRelease(Resource<R> resource, DataSource dataSource) {
//Bitmap.prepareToDraw()
if (resource instanceof Initializable) {
((Initializable) resource).initialize();
}
//去在活动缓存中存储本次需要展示的 Bitmap,并正式展示图片
notifyComplete(result, dataSource);
stage = Stage.ENCODE;
try {
//会去磁盘缓存 Resource
/**
* void encode(DiskCacheProvider diskCacheProvider, Options options) {
* GlideTrace.beginSection("DecodeJob.encode");
* try {
* diskCacheProvider
* .getDiskCache()
* .put(key, new DataCacheWriter<>(encoder, toEncode, options));
* } finally {
* toEncode.unlock();
* GlideTrace.endSection();
* }
* }
*/
if (deferredEncodeManager.hasResourceToEncode()) {
deferredEncodeManager.encode(diskCacheProvider, options);
}
} finally {
if (lockedResource != null) {
lockedResource.unlock();
}
}
}
private void notifyComplete(Resource<R> resource, DataSource dataSource) {
setNotifiedOrThrow();
//回调,会调用 EngineJob.onResourceReady()
callback.onResourceReady(resource, dataSource);
}
}
class EngineJob<R> implements DecodeJob.Callback<R>, Poolable {
public void onResourceReady(Resource<R> resource, DataSource dataSource) {
notifyCallbacksOfResult();
}
void notifyCallbacksOfResult() {
//回调到 Engin.onEngineJobComplete(),在活动缓存中存储数据
engineJobListener.onEngineJobComplete(this, localKey, localResource);
//展示图片
for (final ResourceCallbackAndExecutor entry : copy) {
entry.executor.execute(new CallResourceReady(entry.cb));
}
}
private class CallResourceReady implements Runnable {
private final ResourceCallback cb;
CallResourceReady(ResourceCallback cb) {
this.cb = cb;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// Make sure we always acquire the request lock, then the EngineJob lock to avoid deadlock
// (b/136032534).
synchronized (cb.getLock()) {
synchronized (EngineJob.this) {
if (cbs.contains(cb)) {
//活动缓存计数 +1
engineResource.acquire();
//显示图片
callCallbackOnResourceReady(cb);
removeCallback(cb);
}
decrementPendingCallbacks();
}
}
}
}
void callCallbackOnResourceReady(ResourceCallback cb) {
//回调 SingleRequest.onResourceReady()
cb.onResourceReady(engineResource, dataSource);
}
}
public class Engine implements EngineJobListener, MemoryCache.ResourceRemovedListener, EngineResource.ResourceListener {
public synchronized void onEngineJobComplete(EngineJob<?> engineJob, Key key, EngineResource<?> resource) {
//活动缓存中存储
if (resource != null && resource.isMemoryCacheable()) {
activeResources.activate(key, resource);
}
jobs.removeIfCurrent(key, engineJob);
}
}
以上部分主要工作是在活动缓存中缓存数据,展示图片,缓存 Resource,接下来是具体展示的工作
public final class SingleRequest<R> implements Request, SizeReadyCallback, ResourceCallback {
public void onResourceReady(Resource<?> resource, DataSource dataSource) {
Object received = resource.get();
onResourceReady((Resource<R>) resource, (R) received, dataSource);
}
private void onResourceReady(Resource<R> resource, R result, DataSource dataSource) {
//调用 ImageViewtarget
target.onResourceReady(result, animation);
}
}
public abstract class ImageViewTarget<Z> extends ViewTarget<ImageView, Z>
implements Transition.ViewAdapter {
public void onResourceReady(@NonNull Z resource, @Nullable Transition<? super Z> transition) {
if (transition == null || !transition.transition(resource, this)) {
setResourceInternal(resource);
} else {
maybeUpdateAnimatable(resource);
}
}
private void setResourceInternal(@Nullable Z resource) {
//调用子类 DrawableImageViewTarget.setResource()
setResource(resource);
maybeUpdateAnimatable(resource);
}
}
public class DrawableImageViewTarget extends ImageViewTarget<Drawable> {
//展示图片
protected void setResource(@Nullable Drawable resource) {
view.setImageDrawable(resource);
}
}
至此图片加载完毕,总结一下图片加载的流程。
-
读取网络图片资源
-
将读取的图片存储到磁盘中
-
读取存储在磁盘中的图片
-
将读取的图片进行转换,包括裁剪、采样等,转换为最终将要显示在屏幕的图片
-
将转换的图片存储到 ActiveResources 中
-
显示图片
-
如有需要在磁盘中存储转换后的图片,即 ResourceCache
1.2 读取缓存
对第二次请求的资源会依次从内存和磁盘中读取缓存,缓存中都没有才会去网络加载资源。先从内存中读取,
/** Responsible for starting loads and managing active and cached resources. */ public class Engine implements EngineJobListener, MemoryCache.ResourceRemovedListener, EngineResource.ResourceListener { public <R> LoadStatus load(...){ EngineResource<?> memoryResource; //尝试从内存中读取资源 memoryResource = loadFromMemory(key, isMemoryCacheable, startTime); if (memoryResource == null) { return waitForExistingOrStartNewJob(...); } } private EngineResource<?> loadFromMemory(EngineKey key, boolean isMemoryCacheable, long startTime) { //从活跃内存中获取资源 EngineResource<?> active = loadFromActiveResources(key); if (active != null) { return active; } //从内存中获取文件 EngineResource<?> cached = loadFromCache(key); if (cached != null) { return cached; } return null; } private EngineResource<?> loadFromActiveResources(Key key) { EngineResource<?> active = activeResources.get(key); if (active != null) { active.acquire(); } return active; } private EngineResource<?> loadFromCache(Key key) { EngineResource<?> cached = getEngineResourceFromCache(key); if (cached != null) { cached.acquire(); //将读取的资源再次存放到活跃内存中 activeResources.activate(key, cached); } return cached; } private EngineResource<?> getEngineResourceFromCache(Key key) { //从内存中移除 Resource<?> cached = cache.remove(key); return result; } }
以上是从内存中获取 Resource 的流程,先去活动内存中获取,再去内存中获取,如果内存中存在则将 Resource 移除内存,并将其存入活动内存,如果内存中没有目标图片,开始去磁盘中尝试获取,
public class Engine implements EngineJobListener, MemoryCache.ResourceRemovedListener, EngineResource.ResourceListener {
private <R> LoadStatus waitForExistingOrStartNewJob(...){
//获取调用 DecodeJob.run()
engineJob.start(decodeJob);
}
}
class DecodeJob<R> implements DataFetcherGenerator.FetcherReadyCallback,
Runnable, Comparable<DecodeJob<?>>, Poolable {
public void run() {
runWrapped();
}
//会依次去 ResourceCacheGenerator、DataCacheGenerator、SourceGenerator 中获取资源
private void runWrapped() {
switch (runReason) {
case INITIALIZE:
stage = getNextStage(Stage.INITIALIZE);
currentGenerator = getNextGenerator();
runGenerators();
break;
}
}
private void runGenerators() {
while (!isCancelled
&& currentGenerator != null
&& !(isStarted = currentGenerator.startNext())) {
stage = getNextStage(stage);
currentGenerator = getNextGenerator();
}
}
}
class ResourceCacheGenerator implements DataFetcherGenerator, DataFetcher.DataCallback<Object> {
public boolean startNext() {
cacheFile = helper.getDiskCache().get(currentKey);
}
}
class DataCacheGenerator implements DataFetcherGenerator, DataFetcher.DataCallback<Object> {
public boolean startNext() {
cacheFile = helper.getDiskCache().get(originalKey);
}
}
磁盘缓存会依次读取 ResourceCache、DataCache,如果还是获取不到会去网络中读取,读取完毕后还是会将图片存放到活跃内存中。从 DataCache 中读取图片后的流程,与上面的资源缓存流程一致了。
2.生命周期监听
当 Activity 退出时,需要及时清理 ActiveCache,应用退出时需及时清理 MemoryCache,在具体分析之前,来看一下如何构建一次请求的。
Glide.with(this).load("https://himg.bdimg.com/sys/portrait/item/pp.1.1fdc338e.ric5F8oKJekRIoc8wsplCg?_t=1689664631126").into(imageView);
Glide.with(this) 主要是构建 RequestManager
public class Glide implements ComponentCallbacks2 {
public static RequestManager with(@NonNull FragmentActivity activity) {
return getRetriever(activity).get(activity);
}
private static RequestManagerRetriever getRetriever(@Nullable Context context) {
return Glide.get(context).getRequestManagerRetriever();
}
public RequestManagerRetriever getRequestManagerRetriever() {
return requestManagerRetriever;
}
public static Glide get(@NonNull Context context) {
//做一些初始化的操作
checkAndInitializeGlide(context, annotationGeneratedModule);
return glide;
}
private static void checkAndInitializeGlide(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable GeneratedAppGlideModule generatedAppGlideModule) {
itializing = true;
initializeGlide(context, generatedAppGlideModule);
isInitializing = false;
}
private static void initializeGlide(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable GeneratedAppGlideModule generatedAppGlideModule) {
initializeGlide(context, new GlideBuilder(), generatedAppGlideModule);
}
private static void initializeGlide(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull GlideBuilder builder,
@Nullable GeneratedAppGlideModule annotationGeneratedModule) {
//构建 Glide,其中主要关注 RequestManagerRetriever 即 RequestManager 的构建工厂,为默认的 DEFAULT_FACTORY
Glide glide = builder.build(applicationContext);
//注册组件,应用 onLowMemory() 时回调 Glide.onLowMemory()
applicationContext.registerComponentCallbacks(glide);
Glide.glide = glide;
}
}
public class RequestManagerRetriever implements Handler.Callback {
public RequestManager get(@NonNull FragmentActivity activity) {
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
return get(activity.getApplicationContext());
} else {
assertNotDestroyed(activity);
FragmentManager fm = activity.getSupportFragmentManager();
return supportFragmentGet(activity, fm, /*parentHint=*/ null, isActivityVisible(activity));
}
}
private RequestManager supportFragmentGet(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull FragmentManager fm,
@Nullable Fragment parentHint, boolean isParentVisible) {
SupportRequestManagerFragment current = getSupportRequestManagerFragment(fm, parentHint, isParentVisible);
RequestManager requestManager = current.getRequestManager();
if (requestManager == null) {
Glide glide = Glide.get(context);
/**
* public class SupportRequestManagerFragment extends Fragment {
* private final ActivityFragmentLifecycle lifecycle;
*
* private RequestManager requestManager;
*
* public SupportRequestManagerFragment() {
* this(new ActivityFragmentLifecycle());
* }
*
* public SupportRequestManagerFragment(@NonNull ActivityFragmentLifecycle lifecycle) {
* this.lifecycle = lifecycle;
* }
*
* ActivityFragmentLifecycle getGlideLifecycle() {
* return lifecycle;
* }
* }
*
* public class RequestManager
* implements ComponentCallbacks2, LifecycleListener, ModelTypes<RequestBuilder<Drawable>> {
* public RequestManager(...){
* this(
* glide,
* lifecycle,
* treeNode,
* new RequestTracker(),
* glide.getConnectivityMonitorFactory(),
* context);
* }
*
* RequestManager(...){
* //由 ActivityFragmentLifecycle 管理本组件生命周期
* lifecycle.addListener(this);
* }
* }
*
* class ActivityFragmentLifecycle implements Lifecycle {
* private final Set<LifecycleListener> lifecycleListeners =
* Collections.newSetFromMap(new WeakHashMap<LifecycleListener, Boolean>());
* public void addListener(@NonNull LifecycleListener listener) {
* lifecycleListeners.add(listener);
* }
* }
*/
//到这里可以获知一个 FragmentActivity 绑定一个 SupportRequestManagerFragment,
//一个 SupportRequestManagerFragment 有一个 RequestManager 及 ActivityFragmentLifecycle
//RequestManager 是一个 LifecycleListener 组件,会 add 到 ActivityFragmentLifecycle 中
requestManager =
factory.build(
glide, current.getGlideLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode(), context);
current.setRequestManager(requestManager);
}
return requestManager;
}
private SupportRequestManagerFragment getSupportRequestManagerFragment(
@NonNull final FragmentManager fm, @Nullable Fragment parentHint, boolean isParentVisible) {
//一个 FragmentActivity 绑定一个 SupportRequestManagerFragment
//一个 SupportRequestManagerFragment 绑定一个 RequestManager
SupportRequestManagerFragment current = (SupportRequestManagerFragment) fm.findFragmentByTag(FRAGMENT_TAG);
if (current == null) {
current = new SupportRequestManagerFragment();
fm.beginTransaction().add(current, FRAGMENT_TAG).commitAllowingStateLoss();
current.setRequestManager(requestManager);
}
return current;
}
}
Glide.with(this) 生成一个 RequestManager,做的工作如下
-
初始化 Glide ,初始化 RequestManagerRetriever。
-
查看是否有调用者是否有 SupportRequestManagerFragment,没有就新建并添加到 FragmentManager 中,SupportRequestManagerFragment 可以感知 Activity 的生命周期。
-
创建 RequestManager,并将其与 SupportRequestManagerFragment 绑定,其是一个 LifecycleListener ,会被 add 到 SupportRequestManagerFragment.ActivityFragmentLifecycle 中,
-
到此初步的生命周期监听链形成,Activity –> SupportRequestManagerFragment –> ActivityFragmentLifecycle –> RequestManager
继续向下走,来到 Glide.with(this).load(“”)
public class RequestManager implements ComponentCallbacks2, LifecycleListener, ModelTypes<RequestBuilder<Drawable>> {
//构建 RequestBuilder 用来生成最终的 Request
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> load(@Nullable String string) {
return asDrawable().load(string);
}
public RequestBuilder<Drawable> asDrawable() {
return as(Drawable.class);
}
public <ResourceType> RequestBuilder<ResourceType> as(@NonNull Class<ResourceType> resourceClass) {
return new RequestBuilder<>(glide, this, resourceClass, context);
}
}
public class RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> extends BaseRequestOptions<RequestBuilder<TranscodeType>>
implements Cloneable, ModelTypes<RequestBuilder<TranscodeType>> {
public RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> load(@Nullable String string) {
return loadGeneric(string);
}
private RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> loadGeneric(@Nullable Object model) {
this.model = model;
isModelSet = true;
return this;
}
}
Glide.with(this).load(“”) 生成 RequestBuilder,用来生成具体负责请求的 Request,接下来到 into() 了,开始真正的请求
public class RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> extends BaseRequestOptions<RequestBuilder<TranscodeType>>
implements Cloneable, ModelTypes<RequestBuilder<TranscodeType>> {
public ViewTarget<ImageView, TranscodeType> into(@NonNull ImageView view) {
return into(
glideContext.buildImageViewTarget(view, transcodeClass),
/*targetListener=*/ null,
requestOptions,
Executors.mainThreadExecutor());
}
private <Y extends Target<TranscodeType>> Y into(
@NonNull Y target,
@Nullable RequestListener<TranscodeType> targetListener,
BaseRequestOptions<?> options,
Executor callbackExecutor) {
//具体的生成的 Request 为 SingleRequest
Request request = buildRequest(target, targetListener, options, callbackExecutor);
//将新生成的 Request 交给 RequestManager 管理
requestManager.track(target, request);
}
}
public class RequestManager
implements ComponentCallbacks2, LifecycleListener, ModelTypes<RequestBuilder<Drawable>> {
private final TargetTracker targetTracker = new TargetTracker();
synchronized void track(@NonNull Target<?> target, @NonNull Request request) {
targetTracker.track(target);
requestTracker.runRequest(request);
}
}
public class RequestTracker {
private final Set<Request> requests = Collections.newSetFromMap(new WeakHashMap<Request, Boolean>());
public void runRequest(@NonNull Request request) {
requests.add(request);
//开始请求
request.begin();
}
}
public final class SingleRequest<R> implements Request, SizeReadyCallback, ResourceCallback {
//Responsible for starting loads and managing active and cached resources.
private volatile Engine engine;
public void clear() {
engine.release(toRelease);
}
}
到这里再总结一下,每个请求会有相应的 Request 与之对应,由 RequestManager 负责管理,每个 Request 有一个 Engine(单例) 的引用,Engine 负责管理缓存和加载数据。
这里的生命周期链变为 Activity –> SupportRequestManagerFragment –> ActivityFragmentLifecycle –> RequestManager –> Request –> Engine
到这里生命周期调用链基本呈现出来了,现在看一下 Activity.onDestroy() 时,完整的执行流程
public class SupportRequestManagerFragment extends Fragment {
public void onDestroy() {
lifecycle.onDestroy();
}
}
class ActivityFragmentLifecycle implements Lifecycle {
void onDestroy() {
isDestroyed = true;
for (LifecycleListener lifecycleListener : Util.getSnapshot(lifecycleListeners)) {
lifecycleListener.onDestroy();
}
}
}
public class RequestManager
implements ComponentCallbacks2, LifecycleListener, ModelTypes<RequestBuilder<Drawable>> {
public synchronized void onDestroy() {
requestTracker.clearRequests();
}
public void clearRequests() {
for (Request request : Util.getSnapshot(requests)) {
clearAndRemove(request);
}
}
public boolean clearAndRemove(@Nullable Request request) {
request.clear();
}
}
public final class SingleRequest<R> implements Request, SizeReadyCallback, ResourceCallback {
public void clear() {
engine.release(toRelease);
}
}
public class Engine implements EngineJobListener, MemoryCache.ResourceRemovedListener, EngineResource.ResourceListener {
public void release(Resource<?> resource) {
((EngineResource<?>) resource).release();
}
}
class EngineResource<Z> implements Resource<Z> {
void release() {
boolean release = false;
synchronized (this) {
if (acquired <= 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot release a recycled or not yet acquired resource");
}
if (--acquired == 0) {
release = true;
}
}
//最后一个引用被取消时,完全释放
if (release) {
listener.onResourceReleased(key, this);
}
}
}
public class Engine implements EngineJobListener, MemoryCache.ResourceRemovedListener, EngineResource.ResourceListener {
public void onResourceReleased(Key cacheKey, EngineResource<?> resource) {
//从活跃内存中移除
activeResources.deactivate(cacheKey);
//存放到内存中
if (resource.isMemoryCacheable()) {
cache.put(cacheKey, resource);
} else {
resourceRecycler.recycle(resource, /*forceNextFrame=*/ false);
}
}
}
上面就是 Activity 销毁时,内存中缓存所做的变动了,下面再来看看 APP 销毁。
APP 销毁时内存变动就比较简单粗暴了,直接全部抹除就好了,之间有看到 Glide 时实现 ComponentCallbacks2 接口的,APP 销毁时会回调 onTrimMemory(int level)
public class Glide implements ComponentCallbacks2 {
public void onTrimMemory(int level) {
trimMemory(level);
}
public void trimMemory(int level) {
// Engine asserts this anyway when removing resources, fail faster and consistently
Util.assertMainThread();
for (RequestManager manager : managers) {
manager.onTrimMemory(level);
}
memoryCache.trimMemory(level);
bitmapPool.trimMemory(level);
arrayPool.trimMemory(level);
}
}
3.内存复用策略
Glide 特性之一就是内存复用,内存复用可以防止内存抖动的情况发生,Glide 内存复用主要为 BytePool 和 BitmapPool,先来看 BytePool 的复用。
存储网络资源到 Disk
public class StreamEncoder implements Encoder<InputStream> {
private final ArrayPool byteArrayPool;
public boolean encode(@NonNull InputStream data, @NonNull File file, @NonNull Options options) {
//BytePool 中获取
byte[] buffer = byteArrayPool.get(ArrayPool.STANDARD_BUFFER_SIZE_BYTES, byte[].class);
boolean success = false;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
os = new FileOutputStream(file);
int read;
while ((read = data.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, read);
}
os.close();
success = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "Failed to encode data onto the OutputStream", e);
}
} finally {
if (os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Do nothing.
}
}
//返还给 BytePool
byteArrayPool.put(buffer);
}
return success;
}
}
public final class LruArrayPool implements ArrayPool {
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 4 * 1024 * 1024;
//NavigableMap key 为 size,value 为 size 的计数
private final Map<Class<?>, NavigableMap<Integer, Integer>> sortedSizes = new HashMap<>();
private final KeyPool keyPool = new KeyPool();
//value 为链表结构
private final GroupedLinkedMap<Key, Object> groupedMap = new GroupedLinkedMap<>();
public synchronized <T> T get(int size, Class<T> arrayClass) {
//初次返回 NULL,
//返回 >= size 的 array
Integer possibleSize = getSizesForAdapter(arrayClass).ceilingKey(size);
final Key key;
//false 走 else 分支
if (mayFillRequest(size, possibleSize)) {
key = keyPool.get(possibleSize, arrayClass);
} else {
//创建Key 以 size + arrayClass 标记,equals 方法使用 size+arrayClass
key = keyPool.get(size, arrayClass);
}
return getForKey(key, arrayClass);
}
public synchronized <T> void put(T array) {
Class<T> arrayClass = (Class<T>) array.getClass();
ArrayAdapterInterface<T> arrayAdapter = getAdapterFromType(arrayClass);
int size = arrayAdapter.getArrayLength(array);
int arrayBytes = size * arrayAdapter.getElementSizeInBytes();
if (!isSmallEnoughForReuse(arrayBytes)) {
return;
}
Key key = keyPool.get(size, arrayClass);
groupedMap.put(key, array);
NavigableMap<Integer, Integer> sizes = getSizesForAdapter(arrayClass);
Integer current = sizes.get(key.size);
//记录 size,同类型同 size,计数 +1
sizes.put(key.size, current == null ? 1 : current + 1);
currentSize += arrayBytes;
evict();
}
//groupedMap 中存在则直接返回,不存在则新建一个 byte[]
private <T> T getForKey(Key key, Class<T> arrayClass) {
......
}
private boolean mayFillRequest(int requestedSize, Integer actualSize) {
return actualSize != null
&& (isNoMoreThanHalfFull() || actualSize <= (MAX_OVER_SIZE_MULTIPLE * requestedSize));
}
private NavigableMap<Integer, Integer> getSizesForAdapter(Class<?> arrayClass) {
NavigableMap<Integer, Integer> sizes = sortedSizes.get(arrayClass);
//初次获取一定为 NULL
if (sizes == null) {
sizes = new TreeMap<>();
//保存
sortedSizes.put(arrayClass, sizes);
}
//返回 TreeMap
return sizes;
}
private static final class KeyPool extends BaseKeyPool<Key> {
private static final int MAX_SIZE = 20;
private final Queue<T> keyPool = Util.createQueue(MAX_SIZE);
KeyPool() {}
Key get(int size, Class<?> arrayClass) {
Key result = get();
result.init(size, arrayClass);
return result;
}
@Override
protected Key create() {
return new Key(this);
}
T get() {
T result = keyPool.poll();
if (result == null) {
result = create();
}
return result;
}
public void offer(T key) {
if (keyPool.size() < MAX_SIZE) {
keyPool.offer(key);
}
}
protected Key create() {
return new Key(this);
}
}
}
class GroupedLinkedMap<K extends Poolable, V> {
private final LinkedEntry<K, V> head = new LinkedEntry<>();
//Map 中的 Value 会形成一个循环双向链表
private final Map<K, LinkedEntry<K, V>> keyToEntry = new HashMap<>();
public void put(K key, V value) {
LinkedEntry<K, V> entry = keyToEntry.get(key);
if (entry == null) {
entry = new LinkedEntry<>(key);
//放到队尾
makeTail(entry);
keyToEntry.put(key, entry);
} else {
key.offer();
}
entry.add(value);
}
public V get(K key) {
LinkedEntry<K, V> entry = keyToEntry.get(key);
if (entry == null) {
entry = new LinkedEntry<>(key);
keyToEntry.put(key, entry);
} else {
key.offer();
}
//移到队头
makeHead(entry);
return entry.removeLast();
}
private static class LinkedEntry<K, V> {
@Synthetic final K key;
private List<V> values;
LinkedEntry<K, V> next;
LinkedEntry<K, V> prev;
}
}
大概的结构如下
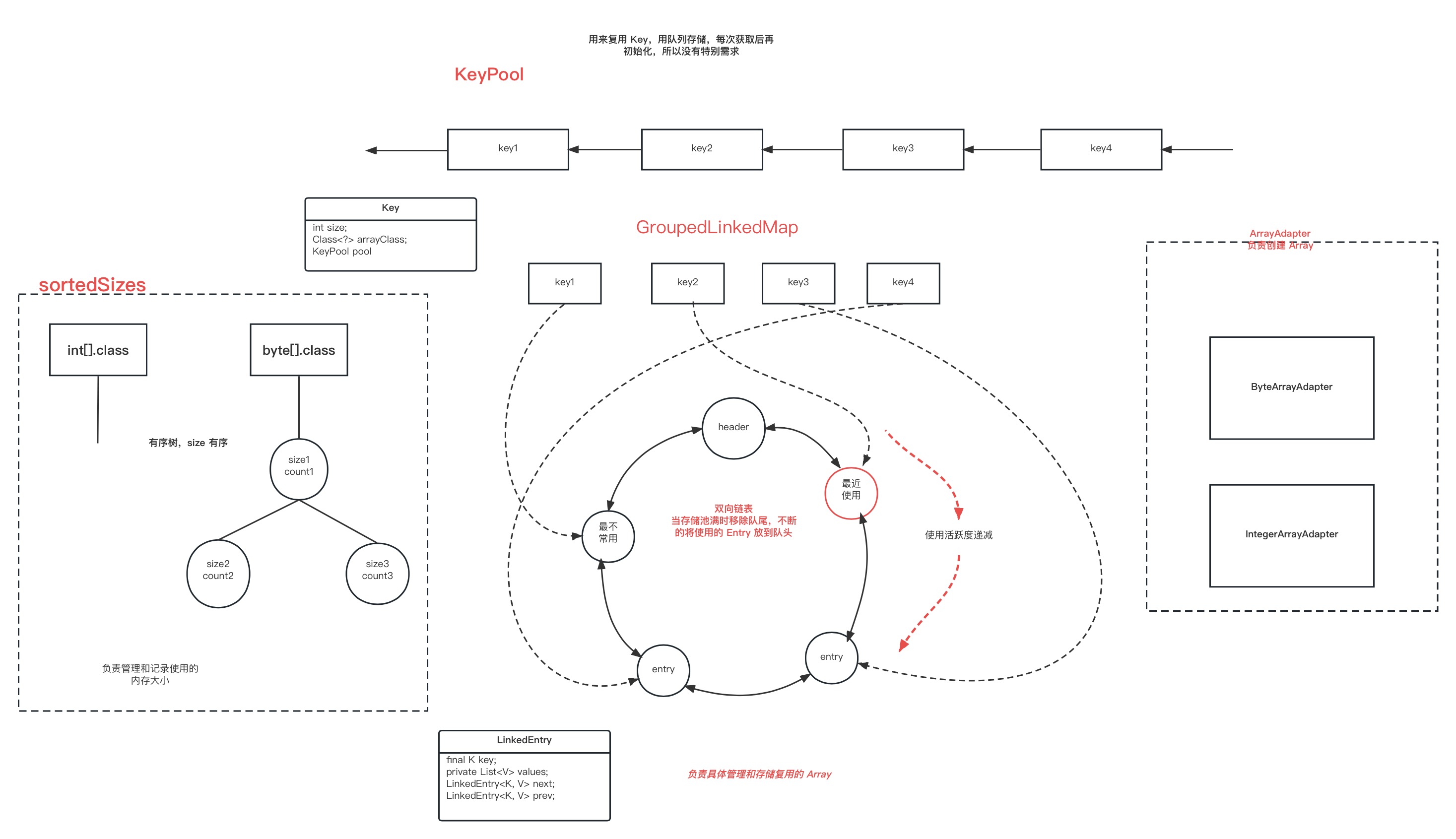
以 arrayPool.get(bufferSize, byte[].class) 为例,复用的流程为:
-
先去 sortedSizes 中查询,key 为 arrayType,返回的是 TreeMap
-
查询是否有 size >= bufferSize,存在则返回 possibleSize
-
使用 possibleSize 初始化 Key
-
依据 Key 查询是否缓存池中存在目标大小的 byte[],不存在则新建
当然实际的逻辑还要更复杂,还要动态管理缓存池的大小,更新最近使用 Entry。
下面再来分析 BitmapPool,Bitmap 的复用。创建 Bitmap 时,可以使用 BitmapFactory.Options.inBitmap 来复用 Bitmap,来看看 Glide 如何复用 Bitmap 的
public final class Downsampler {
private static void setInBitmap(BitmapFactory.Options options, BitmapPool bitmapPool, int width, int height) {
options.inBitmap = bitmapPool.getDirty(width, height, expectedConfig);
}
}
public class LruBitmapPool implements BitmapPool {
public Bitmap getDirty(int width, int height, Bitmap.Config config) {
//获取可用 Bitmap
Bitmap result = getDirtyOrNull(width, height, config);
if (result == null) {
result = createBitmap(width, height, config);
}
return result;
}
private synchronized Bitmap getDirtyOrNull(int width, int height, @Nullable Bitmap.Config config) {
final Bitmap result = strategy.get(width, height, config != null ? config : DEFAULT_CONFIG);
return result;
}
public synchronized void put(Bitmap bitmap) {
final int size = strategy.getSize(bitmap);
strategy.put(bitmap);
}
}
public class SizeConfigStrategy implements LruPoolStrategy {
public Bitmap get(int width, int height, Bitmap.Config config) {
int size = Util.getBitmapByteSize(width, height, config);
Key bestKey = findBestKey(size, config);
Bitmap result = groupedMap.get(bestKey);
if (result != null) {
// Decrement must be called before reconfigure.
decrementBitmapOfSize(bestKey.size, result);
result.reconfigure(width, height, config);
}
return result;
}
}
核心是使用 BitmapFactory.Options.inBitmap 来复用,将使用过的 Bitmap 放进复用池,获取的时候只要获取大于目标 Bitmap 即可
4.大图加载
Glide 默认不会加载原图,而是依据目标 ImageView 或调用者设置的 width and height 来 decode 原图。依据原图的 originWidth, originHeight 和目标图的 width, height 来进行采样
public final class Downsampler {
private static void calculateScaling(...){
final float exactScaleFactor = downsampleStrategy.getScaleFactor(orientedSourceWidth, orientedSourceHeight, targetWidth, targetHeight);
int scaleFactor = rounding == SampleSizeRounding.MEMORY
? Math.max(widthScaleFactor, heightScaleFactor)
: Math.min(widthScaleFactor, heightScaleFactor);
int powerOfTwoSampleSize;
//计算采样率
powerOfTwoSampleSize = Math.max(1, Integer.highestOneBit(scaleFactor));
if (rounding == SampleSizeRounding.MEMORY && powerOfTwoSampleSize < (1.f / exactScaleFactor)) {
powerOfTwoSampleSize = powerOfTwoSampleSize << 1;
}
//设置采样率
options.inSampleSize = powerOfTwoSampleSize;
}
}
好了,到这里四个目标就全部完成了,四个目标走下来,发现 DecodeJob 是很核心中的核心,几乎所有逻辑都是通过它中转。
Tags: android - glide