Android 网络请求库 OkHttp 一
2023-07-06, by alamide
OkHttp 是当前比较热门的网络请求库,具有高可用、易拓展等特性。本次将会去学习一下这个库,学习目标如下:
-
OkHttp 的基本使用
-
追踪一次完整的请求流程
-
OkHttp 做了哪些工作来提升性能(主要是连接池复用方面)
-
OkHttp 的责任链
1.OKHttp 的基本使用
1.1 引入依赖
首先引入 okhttp,这里不引入最新版本,因为最新版本使用 Kotlin,还不是太熟悉
<dependency>
<groupId>com.squareup.okhttp3</groupId>
<artifactId>okhttp</artifactId>
<version>3.14.9</version>
</dependency>
1.2 同步 GET 请求
简单的 GET 请求,获取页面
private static void syncGet() throws IOException {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://localhost:8080/res/index.html")
.get()
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (!response.isSuccessful()) {
throw new IOException("UnExcepted Code " + response.code());
}
final Headers headers = response.headers();
IntStream.range(0, headers.size()).forEach(index -> {
System.out.println(headers.name(index) + ": " + headers.value(index));
});
System.out.println(response.body().string());
}
}
1.3 异步 GET 请求
异步请求,主线程中不用再等待请求的结果,适用于 Android
private static void asyncGet() {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://localhost:8080/res/index.html")
.get()
.build();
client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
System.out.println("UnExcepted IOException");
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
final Headers headers = response.headers();
IntStream.range(0, headers.size()).forEach(index -> {
System.out.println(headers.name(index) + ": " + headers.value(index));
});
System.out.println(response.body().string());
}
});
System.out.println("finish.....");
}
1.4 Header 的设置与获取
在请求时设置 Header ,在获取响应时获取 Header
private static void syncGet() throws IOException {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://localhost:8080/user")
//要求服务器返回 xml 类型的数据
.addHeader("Accept", "application/xml")
.get()
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (!response.isSuccessful()) {
throw new IOException("UnExcepted Code " + response.code());
}
final Headers headers = response.headers();
//获取 Header
final String contentType = headers.get("Content-Type");
System.out.println(contentType);
System.out.println(response.body().string());
}
System.out.println("finish....");
}
1.5 POST 简单 Json 类型的数据
向服务器发送 json 类型的数据
private static void postJson() throws IOException {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
final MediaType APPLICATION_JSON = MediaType.parse("application/json");
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://localhost:8080/user")
.addHeader("Accept", "application/xml")
.post(RequestBody.create(APPLICATION_JSON, "{\"name\":\"alamide\",\"age\":18}"))
.build();
readResponse(client, request);
}
1.6 POST File
向服务器发送文件
private static void postAFile() throws IOException {
final HttpLoggingInterceptor httpLoggingInterceptor = new HttpLoggingInterceptor();
httpLoggingInterceptor.setLevel(HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level.BODY);
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addNetworkInterceptor(httpLoggingInterceptor)
.build();
final MediaType MEDIA_IMAGE = MediaType.parse("image/jpeg");
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://localhost:8080/user/avatar")
.post(RequestBody.create(MEDIA_IMAGE, new File(file)))
.build();
readResponse(client, request);
}
1.7 POST 提交表单数据
向服务器提交表单数据
private static void postForm() throws IOException {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
final FormBody formBody = new FormBody.Builder()
.add("username", "alamide")
.add("age", "18")
.build();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://localhost:8080/user")
.post(formBody)
.build();
readResponse(client, request);
}
1.8 POST Multipart
private static void postMultipart() throws IOException {
final MediaType MEDIA_IMAGE = MediaType.parse("image/jpeg");
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
final MultipartBody multipartBody = new MultipartBody.Builder()
.addFormDataPart("username", "alamide")
.addFormDataPart("age", "18")
.addFormDataPart("avatar",
"avatar.jpeg",
RequestBody.create(MEDIA_IMAGE, new File(file)))
.build();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://localhost:8080/user")
.post(multipartBody)
.build();
readResponse(client, request);
}
1.9 Response Cache
使用缓存机制,缓存数据,需要服务端来配合,通过 Cache-Control 来控制,通常一些静态资源可以缓存,如图片、css等
private static void responseCache() throws IOException {
int cacheSize = 10 * 1024 * 1024;
Cache cache = new Cache(new File(cache_dir), cacheSize);
HttpLoggingInterceptor loggingInterceptor = new HttpLoggingInterceptor();
loggingInterceptor.setLevel(HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level.BODY);
final OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addNetworkInterceptor(loggingInterceptor)
.cache(cache)
.build();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("https://dss0.bdstatic.com/5aV1bjqh_Q23odCf/static/superman/img/weather/icons/a0.png")
.get()
.build();
readResponse(client, request);
}
可以看到,第二次请求时已使用缓存,看一下存储文件中的存储头
https://dss0.bdstatic.com/5aV1bjqh_Q23odCf/static/superman/img/weather/icons/a0.png
GET
0
HTTP/1.1 200
15
server: JSP3/2.0.14
date: Thu, 06 Jul 2023 04:46:49 GMT
content-type: image/png
content-length: 1496
expires: Wed, 02 Aug 2023 06:14:20 GMT
last-modified: Wed, 11 Mar 2020 05:42:17 GMT
etag: "5e687a39-5d8"
cache-control: max-age=2592000
age: 248137
可以看到有 cache-control 项,在超过缓存期限后,重新请求网络,缓存需要服务端配合
1.10 Cancel Call
取消一个未结束的请求,
private static void cancelCall() {
final ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
final OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://httpbin.org/delay/5")
.get()
.build();
final Call call = client.newCall(request);
scheduledExecutorService.schedule(() -> {
call.cancel();
System.out.println("cancel request");
}, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
try (Response response = call.execute()) {
System.out.println(response.body());
readResponse(client, request);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
1.11 设置超时时间
private static void timeout() throws IOException {
final OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
//连接超时时间
.connectTimeout(4, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.writeTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
//读超时时间
.readTimeout(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://httpbin.org/delay/5")
.get()
.build();
readResponse(client, request);
}
1.12 定制每一次 Call
可以配置每一次 Call,使用同一个 Client 即可,这样就可以复用 Socket 连接池了
private static void timeout() throws IOException {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
OkHttpClient client1 = client.newBuilder()
.readTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://httpbin.org/delay/5")
.get()
.build();
readResponse(client1, request);
OkHttpClient client2 = client.newBuilder()
.readTimeout(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
readResponse(client2, request);
}
2.一次完整的请求
追踪一次完整的网络请求,着重点在请求头、请求体、响应头、响应体、拦截器,以及如何复用 Socket,
private static void postForm() throws IOException {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
final FormBody formBody = new FormBody.Builder()
.add("username", "alamide")
.add("age", "18")
.build();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://localhost:8080/user")
.addHeader("Accept", "application/json")
.post(formBody)
.build();
readResponse(client, request);
}
private static void readResponse(OkHttpClient client, Request request) throws IOException {
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (!response.isSuccessful()) {
throw new IOException("UnExcepted Code " + response.code());
}
final Headers headers = response.headers();
final String contentType = headers.get("Content-Type");
System.out.println(contentType);
System.out.println(response.body().string());
}
System.out.println("finish....");
}
Request 封装请求的信息,包括请求行、请求头、请求体
public final class Request {
final HttpUrl url;
final String method;
final Headers headers;
final @Nullable RequestBody body;
}
调用 client.newCall(request) 来封装一次请求,返回 RealCall
final class RealCall implements Call {
//client 用来执行最终的请求
final OkHttpClient client;
private Transmitter transmitter;
//Request 封装请求信息的类
final Request originalRequest;
//标记当前 Call 是否已被执行
private boolean executed;
}
开始调用 execute,开始网络请求
final class RealCall implements Call {
@Override
public Response execute() throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
//下面两行不是重点,是用来检测请求是否超时的,读超时,写超时
transmitter.timeoutEnter();
transmitter.callStart();
try {
//将请求放入队列中
client.dispatcher().executed(this);
//重点来了,开始使用拦截器
return getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
}
public final class Dispatcher {
private final Deque<RealCall> runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
synchronized void executed(RealCall call) {
runningSyncCalls.add(call);
}
}
getResponseWithInterceptorChain() 开始拦截器部分
final class RealCall implements Call {
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
//这里添加我们自己添加的拦截器,client.addInterceptor
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
//重试
interceptors.add(new RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor(client));
//请求头等
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
//缓存
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
//连接
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
//网络
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, transmitter, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
boolean calledNoMoreExchanges = false;
try {
Response response = chain.proceed(originalRequest);
if (transmitter.isCanceled()) {
closeQuietly(response);
throw new IOException("Canceled");
}
return response;
} catch (IOException e) {
calledNoMoreExchanges = true;
throw transmitter.noMoreExchanges(e);
} finally {
if (!calledNoMoreExchanges) {
transmitter.noMoreExchanges(null);
}
}
}
}
重点看看这几行代码,这是 OkHttp 责任链的具体实现,看一下具体怎么操作的
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, transmitter, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
Response response = chain.proceed(originalRequest);
public final class RealInterceptorChain implements Interceptor.Chain {
private final int index;
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors;
@Override
public Response proceed(Request request) throws IOException {
return proceed(request, transmitter, exchange);
}
public Response proceed(Request request, Transmitter transmitter, @Nullable Exchange exchange)
throws IOException {
......
// Call the next interceptor in the chain.
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, transmitter, exchange,
index + 1, request, call, connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout);
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
......
return response;
}
}
使用拦截链来处理正式请求,来看第一个拦截器 RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor 和最后一个拦截器 CallServerInterceptor,
public final class RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request request = chain.request();
//此时 realChain 的 index = 1,而且每一次调用 realChain.proceed() index 都要加一
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
......
while (true) {
......
//可以看看上面 RealInterceptorChain.proceed(),会新建一个 RealInterceptorChain,并且 index = index + 1
//就按照此种方式一直向后执行,直到最后一个拦截器
response = realChain.proceed(request, transmitter, null);
}
......
}
}
来看最后一个拦截器,intercept 中不再调用 realChain.proceed(),调用链结束
public final class CallServerInterceptor implements Interceptor {
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
......
}
}
所以根据上述分析,自定义 Interceptor 时,一定要调用 realChain.proceed(),否则拦截链断裂。
再来看看每个拦截器的具体职责
RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor,负责重试
BridgeInterceptor,主要是用来添加一些通用的 Header,如 Content-Type、Host 等
CacheInterceptor,缓存,查看是否存在缓存数据,如果有缓存数据则调用链结束,不再执行后续拦截器,直接返回缓存数据
ConnectInterceptor,寻找合适的连接,有可复用的就复用,没有就创建新连接
CallServerInterceptor 执行网络请求,并结束调用链,返回请求结果
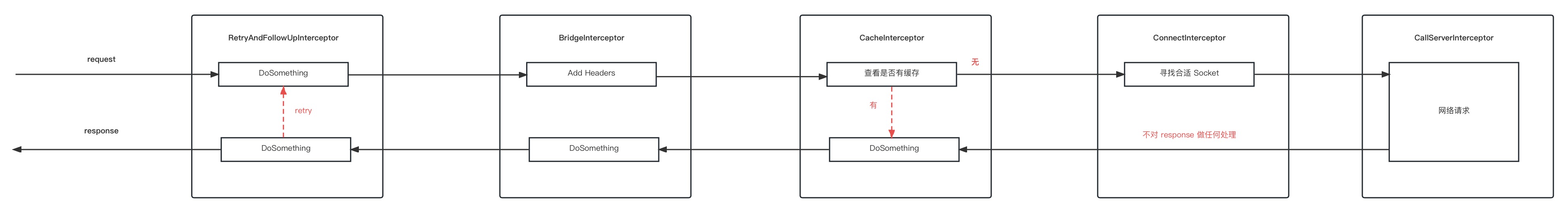
到这里 OkHttp 的拦截器链就学习完毕了,下面再来看看,请求头与请求体
请求头是在 BridgeInterceptor 中设置的,
public final class BridgeInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request userRequest = chain.request();
//此时的 requestBuilder 是含有我们设置的 Header 的,即通过 Request.addHeader() 设置的
Request.Builder requestBuilder = userRequest.newBuilder();
RequestBody body = userRequest.body();
//依据 RequestBody 的类型来设置 Content 相关
if (body != null) {
//如我们的测试,使用的是 FormBody 其 Content-Type 为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded
//我们使用 FormBody 时,不需要自己添加头信息,OkHttp 会自动添加
MediaType contentType = body.contentType();
if (contentType != null) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Type", contentType.toString());
}
//写入 Content-Length
long contentLength = body.contentLength();
if (contentLength != -1) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Length", Long.toString(contentLength));
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Transfer-Encoding");
} else {
requestBuilder.header("Transfer-Encoding", "chunked");
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Length");
}
}
//主机名
if (userRequest.header("Host") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Host", hostHeader(userRequest.url(), false));
}
//默认Connnection 为 keep-alive 即要求保持长连接,因为 OkHttp 希望能够复用 Socket
if (userRequest.header("Connection") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Connection", "Keep-Alive");
}
......
//自动添加 Agent,默认为 okhttp/3.14.9,最好自行添加
if (userRequest.header("User-Agent") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("User-Agent", Version.userAgent());
}
}
}
请求体存放在 RequestBody 中,在向服务器发送数据时 writeTo,具体看看怎么执行写入到 Socket 的 OutputStream 的
public final class CallServerInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
//写入请求头
exchange.writeRequestHeaders(request);
//写入请求体
BufferedSink bufferedRequestBody = Okio.buffer(
exchange.createRequestBody(request, false));
//写数据
request.body().writeTo(bufferedRequestBody);
bufferedRequestBody.close();
}
}
具体的写入在 Http1ExchangeCodec 中,按照指定格式写入就可以了,sink = Okio.buffer(Okio.sink(rawSocket)); 在 RealConnection 中,其实就是对 Socket.getInputStream() 的封装,所以向 sink 中写数据,也就是向 Socket 中写数据
public final class Http1ExchangeCodec implements ExchangeCodec {
@Override
public void writeRequestHeaders(Request request) throws IOException {
String requestLine = RequestLine.get(
request, realConnection.route().proxy().type());
writeRequest(request.headers(), requestLine);
}
//写头部信息
public void writeRequest(Headers headers, String requestLine) throws IOException {
if (state != STATE_IDLE) throw new IllegalStateException("state: " + state);
sink.writeUtf8(requestLine).writeUtf8("\r\n");
for (int i = 0, size = headers.size(); i < size; i++) {
sink.writeUtf8(headers.name(i))
.writeUtf8(": ")
.writeUtf8(headers.value(i))
.writeUtf8("\r\n");
}
sink.writeUtf8("\r\n");
state = STATE_OPEN_REQUEST_BODY;
}
@Override
public Sink createRequestBody(Request request, long contentLength) throws IOException {
if (contentLength != -1L) {
// Stream a request body of a known length.
return newKnownLengthSink();
}
}
private final class KnownLengthSink implements Sink {
......
@Override public void write(Buffer source, long byteCount) throws IOException {
if (closed) throw new IllegalStateException("closed");
checkOffsetAndCount(source.size(), 0, byteCount);
//直接向 Socket 中写数据
sink.write(source, byteCount);
}
......
}
}
再来看看响应头,响应体,读取服务器返回的内容,还是使用 Http1ExchangeCodec,来读取
public final class CallServerInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
if (responseBuilder == null) {
responseBuilder = exchange.readResponseHeaders(false);
}
//这里主要写入响应头等信息
Response response = responseBuilder
.request(request)
.handshake(exchange.connection().handshake())
.sentRequestAtMillis(sentRequestMillis)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
//这里将响应体封装,这里还没有开始读取响应体,只是将获取的接口封装在这里,
//只有调用 response.body().string() 时,才会正式读取
response = response.newBuilder()
.body(exchange.openResponseBody(response))
.build();
}
}
public final class Http1ExchangeCodec implements ExchangeCodec {
@Override
public Response.Builder readResponseHeaders(boolean expectContinue) throws IOException {
......
try {
//读取响应行
StatusLine statusLine = StatusLine.parse(readHeaderLine());
Response.Builder responseBuilder = new Response.Builder()
.protocol(statusLine.protocol)
.code(statusLine.code)
.message(statusLine.message)
//读取响应头
.headers(readHeaders());
......
return responseBuilder;
}
......
}
}
最后来到 OkHttp 的核心了,Socket 的复用,这是 OkHttp 高性能的关键所在
3.Socket 的复用
OkHttp 维持一个 Socket 连接池,来复用 Socket 来提高性能,为什么要复用?因为 TCP 的连接与释放,分别需要三次握手和四次挥手,这是很消耗性能的。
具体的连接相关在 ConnectInterceptor 中,来看看 OkHttp 如何做到复用的
3.1 首次获取连接
首次获取连接,连接池中不存在连接,需要新建连接,并存入到 RealConnectionPool 中
方法调用链
ConnectInterceptor.intercept()
-> Transmitter.newExchange()
-> ExchangeFinder.find()
-> ExchangeFinder.findHealthyConnection()
-> ExchangeFinder.findConnection()
-> RealConnectionPool.transmitterAcquirePooledConnection()
来到 RealConnectionPool.transmitterAcquirePooledConnection()
synchronized (connectionPool) {
if (transmitter.isCanceled()) throw new IOException("Canceled");
if (newRouteSelection) {
// Now that we have a set of IP addresses, make another attempt at getting a connection from
// the pool. This could match due to connection coalescing.
routes = routeSelection.getAll();
if (connectionPool.transmitterAcquirePooledConnection(
address, transmitter, routes, false)) {
foundPooledConnection = true;
result = transmitter.connection;
}
}
if (!foundPooledConnection) {
if (selectedRoute == null) {
selectedRoute = routeSelection.next();
}
//首次请求需要创建新的 RealConnection,此时线程池是空的,
result = new RealConnection(connectionPool, selectedRoute);
connectingConnection = result;
}
//连接 Socket
result.connect(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout, pingIntervalMillis,
connectionRetryEnabled, call, eventListener);
synchronized (connectionPool) {
//存放入连接池
connectionPool.put(result);
}
return result;
}
来到 RealConnection
public void connect(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout,
int pingIntervalMillis, boolean connectionRetryEnabled, Call call,
EventListener eventListener) {
......
connectSocket(connectTimeout, readTimeout, call, eventListener);
......
}
private void connectSocket(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, Call call,
EventListener eventListener) throws IOException {
......
Platform.get().connectSocket(rawSocket, route.socketAddress(), connectTimeout);
......
//封装 Socket.getInputStream()
source = Okio.buffer(Okio.source(rawSocket));
//封装 Socket.getOutputStream()
sink = Okio.buffer(Okio.sink(rawSocket));
}
在 Platform 中的 connect ,就是直接连接 Socket 没有特别处理的
public void connectSocket(Socket socket, InetSocketAddress address, int connectTimeout)
throws IOException {
socket.connect(address, connectTimeout);
}
3.2 非首次获取连接
为方便测试进行如下请求
private static void postForm() throws IOException {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
final FormBody formBody = new FormBody.Builder()
.add("username", "alamide")
.add("age", "18")
.build();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://localhost:8080/user")
.addHeader("Accept", "application/json")
.post(formBody)
.build();
System.out.println("count = " + client.connectionPool().connectionCount());
readResponse(client, request);
System.out.println("count = " + client.connectionPool().connectionCount());
readResponse(client, request);
System.out.println("count = " + client.connectionPool().connectionCount());
readResponse(client, request);
System.out.println("count = " + client.connectionPool().connectionCount());
}
private static void readResponse(OkHttpClient client, Request request) throws IOException {
Response response = client.newCall(request).execute();
if (!response.isSuccessful()) {
throw new IOException("UnExcepted Code " + response.code());
}
response.close();
}
output:
0
1
1
1
因为三次请求的 URL 一致,所以会复用同一个 Socket,下面就来看看具体怎么复用的,
final class ExchangeFinder {
private RealConnection findHealthyConnection(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout,
int writeTimeout, int pingIntervalMillis, boolean connectionRetryEnabled,
boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks) throws IOException {
while (true) {
//寻找合适的连接,有可以复用的就选可复用的,没有就新建
RealConnection candidate = findConnection(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout,
pingIntervalMillis, connectionRetryEnabled);
// If this is a brand new connection, we can skip the extensive health checks.
synchronized (connectionPool) {
if (candidate.successCount == 0 && !candidate.isMultiplexed()) {
return candidate;
}
}
//判断当前连接是否健康
//什么意思呢?因为上面的代码只是寻找有没有 Host 一致的 Socket,
//有可能获取的 Socket 已关闭,或则其它原因不可用c de
//如果不健康的话继续请求新的 connection
if (!candidate.isHealthy(doExtensiveHealthChecks)) {
candidate.noNewExchanges();
continue;
}
return candidate;
}
}
private RealConnection findConnection(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout,
int pingIntervalMillis, boolean connectionRetryEnabled) throws IOException {
......
//尝试获取 Connection
if (connectionPool.transmitterAcquirePooledConnection(address, transmitter, null, false)) {
foundPooledConnection = true;
result = transmitter.connection;
}
if (result != null) {
// If we found an already-allocated or pooled connection, we're done.
return result;
}
}
}
public final class RealConnectionPool {
boolean transmitterAcquirePooledConnection(Address address, Transmitter transmitter,
@Nullable List<Route> routes, boolean requireMultiplexed) {
assert (Thread.holdsLock(this));
//非空
for (RealConnection connection : connections) {
if (requireMultiplexed && !connection.isMultiplexed()) continue;
//判断是否可用
if (!connection.isEligible(address, routes)) continue;
//将当前的 connection 赋值给 transmitter
transmitter.acquireConnectionNoEvents(connection);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
public final class RealConnection extends Http2Connection.Listener implements Connection {
private int allocationLimit = 1;
boolean isEligible(Address address, @Nullable List<Route> routes) {
// 如果绑定当前 Connection 的 transmitter,超过限制,则返回 false
// 非 Http2 请求,allocationLimit 为 1,所以只有前一个请求释放 Connnection 后,才可以被其它请求复用
if (transmitters.size() >= allocationLimit || noNewExchanges) return false;
if (!Internal.instance.equalsNonHost(this.route.address(), address)) return false;
if (address.url().host().equals(this.route().address().url().host())) {
return true; // This connection is a perfect match.
}
return true; // The caller's address can be carried by this connection.
}
}
public final class Transmitter {
void acquireConnectionNoEvents(RealConnection connection) {
assert (Thread.holdsLock(connectionPool));
if (this.connection != null) throw new IllegalStateException();
this.connection = connection;
//transmitters 表示当前 connection 正在被哪些 Transmitter 使用
connection.transmitters.add(new TransmitterReference(this, callStackTrace));
}
}
非首次请求,会先去 ConnectionPool 中查找是否有可能用的 Connnection,一定要是未被占用的
再来做如下请求,就可以看到,虽然三个请求 Url 一致,但是不可以复用,将上面的请求,readResponse 修改一下,不再请求完就关闭 response
private static void readResponse(OkHttpClient client, Request request) throws IOException {
Response response = client.newCall(request).execute();
if (!response.isSuccessful()) {
throw new IOException("UnExcepted Code " + response.code());
}
}
ouput:
0
1
2
3
这就是因为每次请求完,Connection 没有及时释放,可以推断出 response.close() 会去释放连接,来看一下 close() 时究竟做了什么
public final class Response implements Closeable {
@Override
public void close() {
if (body == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("response is not eligible for a body and must not be closed");
}
body.close();
}
}
body 在 CallServerInterceptor 里被封装了一次
public final class CallServerInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
response = response.newBuilder()
.body(exchange.openResponseBody(response))
.build();
}
}
public final class Exchange {
public ResponseBody openResponseBody(Response response) throws IOException {
try {
eventListener.responseBodyStart(call);
String contentType = response.header("Content-Type");
long contentLength = codec.reportedContentLength(response);
Source rawSource = codec.openResponseBodySource(response);
ResponseBodySource source = new ResponseBodySource(rawSource, contentLength);
return new RealResponseBody(contentType, contentLength, Okio.buffer(source));
} catch (IOException e) {
eventListener.responseFailed(call, e);
trackFailure(e);
throw e;
}
}
IOException bodyComplete(long bytesRead, boolean responseDone, boolean requestDone, @Nullable IOException e) {
if (e != null) {
trackFailure(e);
}
if (requestDone) {
if (e != null) {
eventListener.requestFailed(call, e);
} else {
eventListener.requestBodyEnd(call, bytesRead);
}
}
if (responseDone) {
if (e != null) {
eventListener.responseFailed(call, e);
} else {
eventListener.responseBodyEnd(call, bytesRead);
}
}
return transmitter.exchangeMessageDone(this, requestDone, responseDone, e);
}
final class ResponseBodySource extends ForwardingSource {
public long read(Buffer sink, long byteCount) throws IOException {
if (newBytesReceived == contentLength) {
complete(null);
}
}
public void close() throws IOException {
complete(null);
}
IOException complete(@Nullable IOException e) {
if (completed) return e;
completed = true;
return bodyComplete(bytesReceived, true, false, e);
}
}
}
在 response 读取完毕或关闭后,都回去执行 bodyComplete,最终调用 transmitter.exchangeMessageDone()
public final class Transmitter {
IOException exchangeMessageDone(
Exchange exchange, boolean requestDone, boolean responseDone, @Nullable IOException e) {
e = maybeReleaseConnection(e, false);
}
IOException maybeReleaseConnection(@Nullable IOException e, boolean force) {
releaseConnectionNoEvents();
}
Socket releaseConnectionNoEvents() {
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0, size = this.connection.transmitters.size(); i < size; i++) {
Reference<Transmitter> reference = this.connection.transmitters.get(i);
if (reference.get() == this) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
if (index == -1) throw new IllegalStateException();
RealConnection released = this.connection;
//释放,当前 Transmitter 与 Connection 解除绑定
released.transmitters.remove(index);
}
}
得出结论,在数据读取完毕或主动关闭 response 后,connection 可用
4.Socket 的清理
虽然 Socket 复用会节省一定的资源,但是 Socket 本身也暂用较多的资源,需要及时关闭不可用 Socket 或 长时间未使用的 Socket 以释放资源,
public final class RealConnectionPool {
/**
* 核心线程数设置为 0,表示没有处理任务时销毁线程池,即不保留核心线程
**/
private static final Executor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0 /* corePoolSize */,
Integer.MAX_VALUE /* maximumPoolSize */, 60L /* keepAliveTime */, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp ConnectionPool", true));
//最多空闲的线程数 5
private final int maxIdleConnections;
//存活时长 5 minutes
private final long keepAliveDurationNs;
private final Runnable cleanupRunnable = () -> {
while (true) {
long waitNanos = cleanup(System.nanoTime());
if (waitNanos == -1) return;
if (waitNanos > 0) {
long waitMillis = waitNanos / 1000000L;
waitNanos -= (waitMillis * 1000000L);
synchronized (RealConnectionPool.this) {
try {
//等待指定时间唤醒,释放锁
RealConnectionPool.this.wait(waitMillis, (int) waitNanos);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
}
}
};
//连接池
private final Deque<RealConnection> connections = new ArrayDeque<>();
//是否正在清理
boolean cleanupRunning;
//向连接池中新增连接时,开启清理工作
void put(RealConnection connection) {
assert (Thread.holdsLock(this));
if (!cleanupRunning) {
//标记为正在清理
cleanupRunning = true;
executor.execute(cleanupRunnable);
}
connections.add(connection);
}
long cleanup(long now) {
int inUseConnectionCount = 0;
int idleConnectionCount = 0;
RealConnection longestIdleConnection = null;
long longestIdleDurationNs = Long.MIN_VALUE;
// Find either a connection to evict, or the time that the next eviction is due.
synchronized (this) {
for (Iterator<RealConnection> i = connections.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
RealConnection connection = i.next();
// If the connection is in use, keep searching.
if (pruneAndGetAllocationCount(connection, now) > 0) {
inUseConnectionCount++;
continue;
}
idleConnectionCount++;
// If the connection is ready to be evicted, we're done.
long idleDurationNs = now - connection.idleAtNanos;
if (idleDurationNs > longestIdleDurationNs) {
longestIdleDurationNs = idleDurationNs;
longestIdleConnection = connection;
}
}
//如果最长空闲 Connection 的空闲时长 > 5 minutes
//或空闲的 Connection 数 > 5
if (longestIdleDurationNs >= this.keepAliveDurationNs
|| idleConnectionCount > this.maxIdleConnections) {
//移除 connection
connections.remove(longestIdleConnection);
} else if (idleConnectionCount > 0) {//没有立即要清理的 Connection
// 返回下一需要清理的 Connection 的等待时间
return keepAliveDurationNs - longestIdleDurationNs;
} else if (inUseConnectionCount > 0) {//没有需要清理的 Connection,也没有空闲的 Connection
return keepAliveDurationNs;
} else {
// 没有 Connection
cleanupRunning = false;
return -1;
}
}
closeQuietly(longestIdleConnection.socket());
// Cleanup again immediately.
return 0;
}
//查看 Connection 是否绑定有效的 Transmitter
private int pruneAndGetAllocationCount(RealConnection connection, long now) {
List<Reference<Transmitter>> references = connection.transmitters;
for (int i = 0; i < references.size(); ) {
//弱引用,可能被 GC 回收
Reference<Transmitter> reference = references.get(i);
if (reference.get() != null) {
i++;
continue;
}
// We've discovered a leaked transmitter. This is an application bug.
TransmitterReference transmitterRef = (TransmitterReference) reference;
String message = "A connection to " + connection.route().address().url()
+ " was leaked. Did you forget to close a response body?";
Platform.get().logCloseableLeak(message, transmitterRef.callStackTrace);
references.remove(i);
connection.noNewExchanges = true;
// If this was the last allocation, the connection is eligible for immediate eviction.
if (references.isEmpty()) {
connection.idleAtNanos = now - keepAliveDurationNs;
return 0;
}
}
return references.size();
}
}
清理工作的流程是开启线程,判断是否有空闲且超时的 Connection,如就移除连接池,并关闭
5.异步执行
逻辑比较简单,这里就直接贴一下代码执行流程
final class RealCall implements Call {
@Override
public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
transmitter.callStart();
client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback));
}
}
public final class Dispatcher {
private final Deque<AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
synchronized (this) {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call);
// Mutate the AsyncCall so that it shares the AtomicInteger of an existing running call to
// the same host.
if (!call.get().forWebSocket) {
AsyncCall existingCall = findExistingCallWithHost(call.host());
if (existingCall != null) call.reuseCallsPerHostFrom(existingCall);
}
}
promoteAndExecute();
}
public synchronized ExecutorService executorService() {
if (executorService == null) {
//核心线程数为 0
executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp Dispatcher", false));
}
return executorService;
}
private boolean promoteAndExecute() {
assert (!Thread.holdsLock(this));
List<AsyncCall> executableCalls = new ArrayList<>();
boolean isRunning;
synchronized (this) {
for (Iterator<AsyncCall> i = readyAsyncCalls.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
AsyncCall asyncCall = i.next();
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() >= maxRequests) break; // Max capacity.
if (asyncCall.callsPerHost().get() >= maxRequestsPerHost) continue; // Host max capacity.
i.remove();
asyncCall.callsPerHost().incrementAndGet();
executableCalls.add(asyncCall);
runningAsyncCalls.add(asyncCall);
}
isRunning = runningCallsCount() > 0;
}
for (int i = 0, size = executableCalls.size(); i < size; i++) {
AsyncCall asyncCall = executableCalls.get(i);
asyncCall.executeOn(executorService());
}
return isRunning;
}
}
final class RealCall implements Call {
public abstract class NamedRunnable implements Runnable {
protected final String name;
public NamedRunnable(String format, Object... args) {
this.name = Util.format(format, args);
}
public final void run() {
String oldName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
Thread.currentThread().setName(name);
try {
execute();
} finally {
Thread.currentThread().setName(oldName);
}
}
protected abstract void execute();
}
final class AsyncCall extends NamedRunnable {
void executeOn(ExecutorService executorService) {
......
executorService.execute(this);
......
}
protected void execute() {
//这里与同步请求流程一致
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
}
}
6.小结
本次学习主要着重点在 Socket 的复用与释放,东西有点多,后面再从架构方面分析一下,相关类的职责。
Tags: android - okhttp